API 예외 처리 - 시작
- API는 HTML과 다르게 처리해야 한다.
- 오류 페이지는 단순히 오류 화면만 보여주면 끝이다.
- API는 각 오류 상황에 맞는 오류 응답 스펙을 정하고, JSON으로 데이터를 내려주어야 한다.
컨트롤러 생성
- 테스트를 위해 간단한 API 컨트롤러를 만들어 보자.
package hello.exception.api;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class ApiExceptionController {
@GetMapping("/api/members/{id}")
public MemberDto getMember(@PathVariable("id") String id) {
if (id.equals("ex")) {
throw new RuntimeException("잘못된 사용자");
}
return new MemberDto(id, "hello " + id);
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
static class MemberDto {
private String memberId;
private String name;
}
}테스트
- API 테스트 툴로 API를 테스트해보자.
포스트맨이나Thunder Client로 테스트해보자.
http://localhost:8080/api/members/test로 테스트 해보자.
{
"memberId": "test",
"name": "hello test"
}http://localhost:8080/api/members/ex로 테스트를 해보자.- json 결과는 뜨지 않고 갑자기 왠 html이 반환된다.
- 사실 이 html은
RuntimeException때문에 500 취급되는 에러 페이지가 반환된 결과다.
API 응답 추가
- 하지만 우리는 API 오류가 발생하면 그 결과가 json이길 원한다.
- ErrorPageController에 API 응답을 추가해보자.
produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE- 클라이언트가 요청하는 HTTP Header의
Accept의 값이application/json일 때 해당 메서드가 호출된다는 것이다.
- 클라이언트가 요청하는 HTTP Header의
@RequestMapping(value = "/error-page/500", produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> errorPage500Api(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
log.info("API errorPage 500");
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
Exception ex = (Exception) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION);
result.put("status", request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_STATUS_CODE));
result.put("message", ex.getMessage());
Integer statusCode = (Integer) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_STATUS_CODE);
return new ResponseEntity(result, HttpStatus.valueOf(statusCode));
}- 이제 서버를 실행하고 다시
http://localhost:8080/api/members/ex로 테스트를 해보자.- 드디어 API 오류 발생 시에는 json이 반환된다.
- 만약 아직도 html로 반환된다면 요청할 때 HTTP 헤더의
Accept가application/json인지 확인해보자. - API 응답 추가한 것 때문에 페이지가 안 되는 건 아니겠지 싶으면 브라우저로 접속해보자.
http://localhost:8080/error-ex로 접속해보면 여전히 오류 페이지가 잘 나오는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
{
"message": "잘못된 사용자",
"status": 500
}API 예외 처리 - 스프링 부트 기본 오류 처리
- API 예외 처리도 스프링 부트가 제공하는 기본 오류 방식을 사용할 수 있다.
- 이는
BasicErrorController에서/error에 대해 처리하는errorHtml()과error()를 확인해보면 알 수 있다.errorHtml()은 이름 그대로 HTTP 헤더의Accept가text/html인 경우에 동작한다.error()는 그 외의 경우에ResponseEntity로 HTTP 바디에 json 데이터를 반환한다.
스프링 부트의 예외 처리
- 스프링 부트의 기본 설정은 오류 발생시
/error를 오류 페이지로 요청한다. BasicErrorController를 사용하도록WebServerCustomizer의@Component를 주석처리 히자.- 그런 다음에
http://localhost:8080/api/members/ex를 호출해보면 자세한 오류를 확인할 수 있다.
{
"timestamp": "2025-02-01T06:54:41.528+00:00",
"status": 500,
"error": "Internal Server Error",
"exception": "java.lang.RuntimeException",
"path": "/api/members/ex"
}Html 페이지 vs API 오류
BasicErrorController를 확장하면 JSON 메시지도 변경할 수 있다.- 다만 API 오류는 조금 뒤에 설명할
@ExceptionHandler라는 것이 제공하는 기능을 사용하는 것이 더 좋다.- 그러니 이런 방법도 있구나 정도만 이해하면 된다.
- 스프링 부트가 제공하는
BasicErrorController는 HTML 페이지를 제공하는 경우에는 매우 편리하다.- 4xx,5xx 등등 모두 잘 처리해준다.
- 다만 API 오류 처리에는 그리 적합하지는 않다.
- API마다 각각의 컨트롤러나 예외마다 서로 다른 응답 결과를 출력해야 할 수도 있다.
API 예외 처리 - HandlerExceptionResolver 시작
- 만약의 상황의 가정을 세워보자.
- IllegalArgumentException이 발생하면 HTTP 상태 코드를 400으로 반환하고 싶다.
ApiExceptionController의 getMember를 수정해보자.
@GetMapping("/api/members/{id}")
public MemberDto getMember(@PathVariable("id") String id) {
if (id.equals("ex")) {
throw new RuntimeException("잘못된 사용자");
}
if (id.equals("bad")) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("잘못된 입력 값");
}
return new MemberDto(id, "hello " + id);
}http://localhost:8080/api/members/bad를 호출해보자.- 내가 원했던 결과는 400인데 500으로 반환된다.
{
"timestamp": "2025-02-01T07:02:11.541+00:00",
"status": 500,
"error": "Internal Server Error",
"exception": "java.lang.IllegalArgumentException",
"path": "/api/members/bad"
}HandlerExceptionResolver
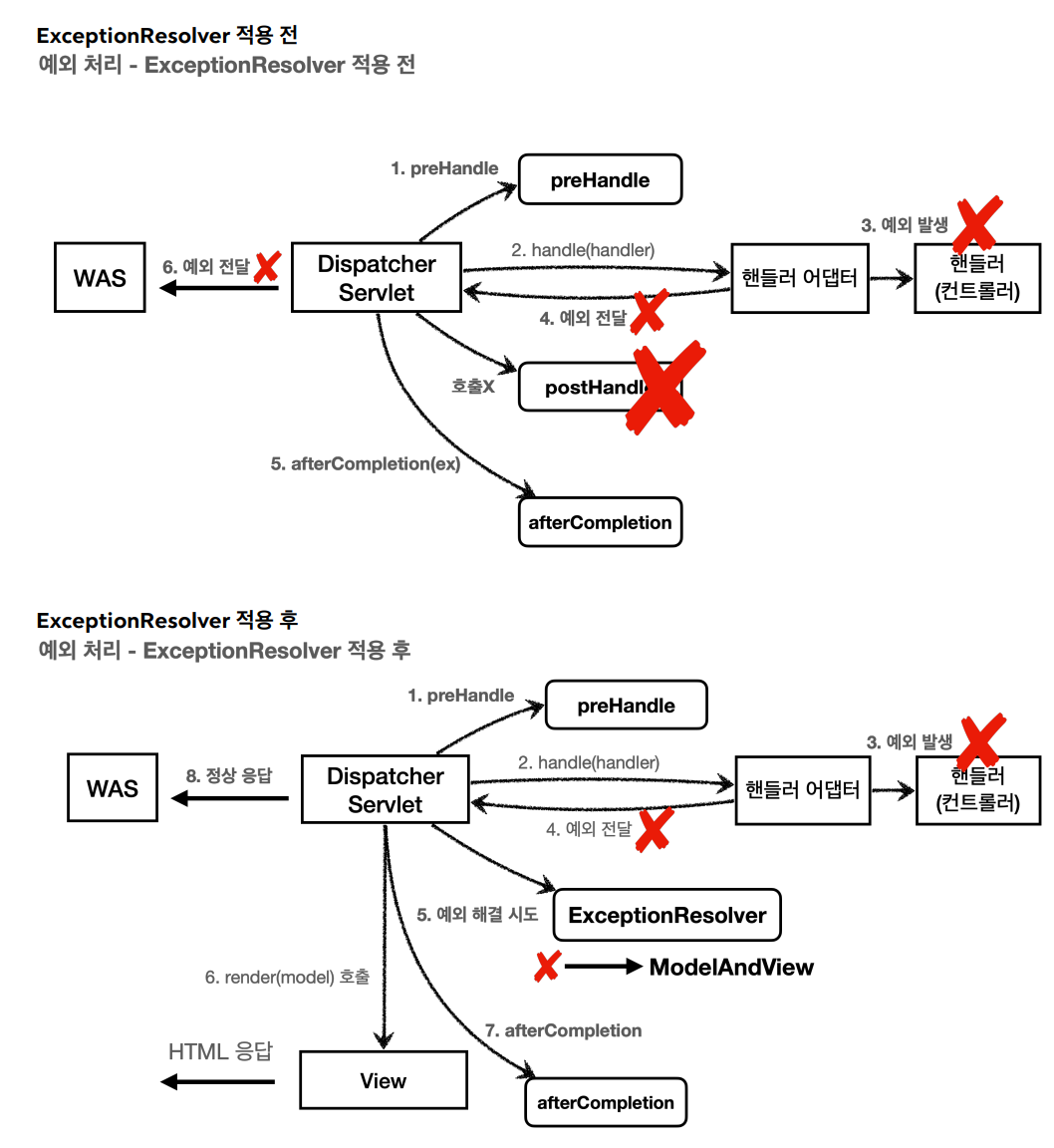
- 스프링 MVC는 컨트롤러(핸들러) 밖으로 예외가 던져진 경우 예외를 해결하고, 동작을 새로 정의할 수 있는 방법을 제공한다.
- 컨트롤러 밖으로 던져진 예외를 해결하고, 동작 방식을 변경하고 싶으면 HandlerExceptionResolver를 사용하면 된다.
- 줄여서
ExceptionResolver라 한다.
- 줄여서
다만
ExceptionResolver로 예외를 해결해도postHandle()은 호출되지 않는다.인터페이스를 확인해보자.
handler- 핸들러(컨트롤러) 정보
Exception ex- 핸들러(컨트롤러)에서 발생한 발생한 예외
public interface HandlerExceptionResolver {
ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex);
}테스트를 위한 리졸버를 만들어보자.
package hello.exception.resolver;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import java.io.IOException;
@Slf4j
public class MyHandlerExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver {
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) {
try {
if (ex instanceof IllegalArgumentException) {
log.info("IllegalArgumentException resolver to 400");
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST, ex.getMessage());
return new ModelAndView();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("resolver ex", e);
}
return null;
}
}ExceptionResolver가ModelAndView를 반환한다.- 마치 try-catch처럼
Exception을 처리해서 정상 흐름처럼 변경하는 것이 목적이다. - 이름 그대로 Exception을 Resolver(해결)하는 것이 목적이다.
- 마치 try-catch처럼
반환 값에 따른 동작 방식
HandlerExceptionResolver의 반환 값에 따른DispatcherServlet의 동작 방식은 다음과 같다.- 빈
ModelAndView- 빈
ModelAndView를 반환하면 뷰를 렌더링 하지 않고, 정상 흐름으로 서블릿이 리턴된다.
- 빈
ModelAndView지정ModelAndView에 View, Model 등의 정보를 지정해서 반환하면 뷰를 렌더링 한다.
nullnull을 반환하면, 다음ExceptionResolver를 찾아서 실행한다.- 만약 처리할 수 있는
ExceptionResolver가 없으면 예외 처리가 안 되고, 기존에 발생한 예외를 서블릿 밖으로 던진다.
- 빈
ExceptionResolver 활용
- 예외 상태 코드 변환
- 예외를
response.sendError(xxx)호출로 변경해서 서블릿에서 상태 코드에 따른 오류를 처리하도록 위임한다. - 이후 WAS는 서블릿 오류 페이지를 찾아서 내부 호출을 진행한다.
- 예시 : 스프링 부트 기본 설정인
/error호출
- 예외를
- 뷰 템플릿 처리
ModelAndView에 값을 채워서 예외에 따른 새로운 오류 화면 뷰를 렌더링 해서 제공한다.
- API 응답 처리
response.getWriter().println("hello");처럼 HTTP 응답 바디에 직접 데이터를 넣어줄 수도 있다.- JSON으로 응답하면 API 응답 처리를 할 수 있다.
WebConfig에 리졸버를 추가하자.
- 리졸버를 추가할 때는
extendHandlerExceptionResolvers나configureHandlerExceptionResolvers로 추가한다.- 다만
configureHandlerExceptionResolvers를 사용하면 스프링이 기본으로 제공하는ExceptionResolver가 제거된다. extendHandlerExceptionResolvers를 사용하는 것이 좋다.
- 다만
@Override
public void extendHandlerExceptionResolvers(List<HandlerExceptionResolver> resolvers) {
resolvers.add(new MyHandlerExceptionResolver());
}API 예외 처리 - HandlerExceptionResolver 활용
- 예외가 발생하면 WAS까지 예외가 던져지고, WAS에서 오류 페이지 정보를 찾아서 다시
/error를 호출하는 과정은 너무 복잡하다. ExceptionResolver를 활용하면 예외가 발생했을 때 이런 복잡한 과정 없이 해결할 수 있다.
사용자 정의 예외 추가
package hello.exception.exception;
public class UserException extends RuntimeException {
public UserException() {
super();
}
public UserException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public UserException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public UserException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
protected UserException(String message, Throwable cause, boolean enableSuppression, boolean writableStackTrace) {
super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace);
}
}ApiExceptionController의 getMember를 수정하자.
@GetMapping("/api/members/{id}")
public MemberDto getMember(@PathVariable("id") String id) {
if (id.equals("ex")) {
throw new RuntimeException("잘못된 사용자");
}
if (id.equals("bad")) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("잘못된 입력 값");
}
if (id.equals("user-ex")) {
throw new UserException("사용자 오류");
}
return new MemberDto(id, "hello " + id);
}UserException을 처리하기 위한 리졸버를 만들어보자.
package hello.exception.resolver;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import hello.exception.exception.UserException;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Slf4j
public class UserHandlerExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver {
private final ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) {
try {
if (ex instanceof UserException) {
log.info("UserException resolver to 400");
String acceptHeader = request.getHeader("accept");
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST); //400 에러로 반환
if ("application/json".equals(acceptHeader)) {
Map<String, Object> errorResult = new HashMap<>();
errorResult.put("ex", ex.getClass());
errorResult.put("message", ex.getMessage());
String result = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(errorResult);
response.setContentType("application/json");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(result);
return new ModelAndView();
} else {
//text/html인 경우
return new ModelAndView("error/400");
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("resolver ex", e);
}
return null;
}
}Accept가application/json이라면 결과를 json으로 반환하게 했다.Accept가text/html이라면 결과를 페이지로 반환하게 했다.
WebConfig에 리졸버를 추가하자.
@Override
public void extendHandlerExceptionResolvers(List<HandlerExceptionResolver> resolvers) {
resolvers.add(new MyHandlerExceptionResolver());
resolvers.add(new UserHandlerExceptionResolver());
}테스트
http://localhost:8080/api/members/user-ex를 호출해보자.Accept를application/json으로 해서 호출하면 json으로 결과가 반환된다.
{
"ex": "hello.exception.exception.UserException",
"message": "사용자 오류"
}그런데 이 과정도 사실 쉬운 것은 아니다.
ExceptionResolver를 사용하지 예외 처리가 깔끔해졌다.- 다만 직접
ExceptionResolver를 구현하려고 하니 상당히 복잡하다.- 그러니 스프링이 기본적으로 제공하는
ExceptionResolver를 사용하자.
- 그러니 스프링이 기본적으로 제공하는
API 예외 처리 - 스프링이 제공하는 ExceptionResolver 1
- 스프링 부트에서는 기본적으로 제공하는
ExceptionHandler가 있다.HandlerExceptionResolverComposite에 아래 순서로 등록되어 있다. (우선순위 기준)ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver
@ExceptionHandler를 처리한다.- API 예외 처리는 대부분
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver로 해결한다. 2.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver - HTTP 상태 코드를 지정해준다.
- 예시 :
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)3.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver - 스프링 내부 기본 예외를 처리한다.
ResponseStatusExceptionResolver
ResponseStatusExceptionResolver는 예외에 따라서 HTTP 상태 코드를 지정해주는 역할을 한다.@ResponseStatus가 달려있는 예외ResponseStatusException예외
사용자 정의 예외 추가
package hello.exception.exception;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
@ResponseStatus(code = HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST, reason = "잘못된 요청 오류")
public class BadRequestException extends RuntimeException {
}ApiExceptionController에 메소드 추가
@GetMapping("/api/response-status-ex1")
public String responseStatusEx1() {
throw new BadRequestException();
}테스트
http://localhost:8080/api/response-status-ex1?message를 호출하면 아래와 같은 결과를 얻을 수 있다.
{
"timestamp": "2025-02-01T07:36:11.191+00:00",
"status": 400,
"error": "Bad Request",
"exception": "hello.exception.exception.BadRequestException",
"message": "잘못된 요청 오류",
"path": "/api/response-status-ex1"
}- 메시지를 변경할 수도 있다.
- ` reason = “잘못된 요청 오류”
대신에reason = “error.bad”`라고 작성해보자. messages.properties에서 해당 메시지를 찾아서 반환해준다.error.bad=잘못된 요청 오류입니다. 메시지 사용
- ` reason = “잘못된 요청 오류”
사용자 정의 예외가 아닌 경우
- 사용자 정의 예외일 경우에는
@ResponseStatus를 사용해서 상태 코드를 바꿀 수 있었다. - 하지만 이미 정의되어 있는 예외의 경우에는 상태 코드를 바꿀 수 없기 때문에
ResponseStatusException를 활용해야 한다.
@GetMapping("/api/response-status-ex2")
public String responseStatusEx2() {
throw new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND, "error.bad", new IllegalArgumentException());
}API 예외 처리 - 스프링이 제공하는 ExceptionResolver 2
DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver는 스프링 내부에서 발생하는 스프링 예외를 해결한다.- 정수형 데이터가 필요한데 문자형 데이터를 입력한 경우에 발생하는
TypeMismatchException를 예시로 들 수 있다. - 스프링 내부에서는 500 오류가 발생할 것이다.
- 하지만
DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver가 이것을 500 오류가 아니라 HTTP 상태 코드 오류로 변경한다.
- 하지만
- 왜냐하면
DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver.handleTypeMismatch에서 확인 가능하듯이response.sendError()를 호출하기 때문이다.
테스트용 메소드 만들기
@GetMapping("/api/default-handler-ex")
public String defaultException(@RequestParam Integer data) {
return "ok";
}테스트
- 실제로
http://localhost:8080/api/default-handler-ex?data=hello&message를 호출해보면 아래와 같이 반환한다.
{
"timestamp": "2025-02-01T07:49:55.817+00:00",
"status": 400,
"error": "Bad Request",
"exception": "org.springframework.web.method.annotation.MethodArgumentTypeMismatchException",
"message": "Method parameter 'data': Failed to convert value of type 'java.lang.String' to required type 'java.lang.Integer'; For input string: \"hello\"",
"path": "/api/default-handler-ex"
}그래도 아직 남은 문제점
- 그런데
HandlerExceptionResolver를 직접 사용하는 것은 어렵다. - 왜냐하면 API 오류 응답의 경우에는 HTTP 응답에 직접 데이터를 넣어야 해서 매우 불편하고 번거롭기 때문이다.
- 게다가
ModelAndView를 반환해야 하는 것도 API에는 적합하지 않다.
- 게다가
- 그래서 스프링은 이 문제를 해결하기 위해
@ExceptionHandler라는 기능을 제공한다.ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver에 해당한다.
API 예외 처리 - @ExceptionHandler
HTML 화면 오류 vs API 오류
- 웹 브라우저에 HTML 화면을 제공할 때는 오류가 발생하면
BasicErrorController를 사용하는게 편하다. - API의 경우에는 각 시스템마다 응답의 모양도 다르고 스펙도 모두 다르다.
- 그래서 공통된 처리를 진행하는
BasicErrorController는 적합하지 않다. - 그렇다고
HandlerExceptionResolver를 직접 구현하는 것도 어려운 것이 사실이다.
- 그래서 공통된 처리를 진행하는
API 예외처리의 문제점
HandlerExceptionResolver에서는ModelAndView를 반환해야 했다.- 응답을 json으로 반환해야 하는 API에는 적합하지 않다.
- API 응답을 위해서
HttpServletResponse에 직접 응답 데이터를 넣어주었다.- 매우 귀찮고 번거롭다.
- 서비스의 복잡도가 높거나 규모가 커지면 감당하기 어렵다.
- 특정 컨트롤러에서만 발생하는 예외를 별도로 처리하기 어렵다.
- 발생하는 예외의 종류는 같으나 컨트롤러가 다를 때 각각 다른 방식으로 처리하기가 어렵다.
그래서 나타난 @ExceptionHandler
- 이렇게 어려운 API 예외 처리를 위해 스프링에서는
@ExceptionHandler애노테이션을 제공한다.- 이것이 바로
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver를 활용한 방식이다.
- 이것이 바로
- 스프링은
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver를 기본으로 제공하며, 또한 우선순위도 가장 높다.- 그래서 실무에서 사용하는 API 예외 처리 방식에는 대부분 이 기능을 사용한다.
API 응답 객체 생성
- API 응답을 위해 공통으로 사용할 객체를 만들어보자.
package hello.exception.exhandler;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class ErrorResult {
private String code;
private String message;
}API 컨트롤러 v2 생성
- 이번에는 API 응답 객체를 사용하는 API 컨트롤러를 만들어보자.
- API 동작 방식은
ApiExceptionController과 동일하다. - 다만 API의 결과를 반환할 때 방금 만든 API 응답 객체를 사용하게 했다.
- API 동작 방식은
package hello.exception.exhandler;
import hello.exception.exception.UserException;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class ApiExceptionV2Controller {
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
@ExceptionHandler(IllegalArgumentException.class)
public ErrorResult illegalExHandle(IllegalArgumentException e) {
log.error("[exceptionHandle] ex", e);
return new ErrorResult("BAD", e.getMessage());
}
@ExceptionHandler
public ResponseEntity<ErrorResult> userExHandle(UserException e) {
log.error("[exceptionHandle] ex", e);
ErrorResult errorResult = new ErrorResult("USER-EX", e.getMessage());
return new ResponseEntity<>(errorResult, HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
@ExceptionHandler
public ErrorResult exHandle(Exception e) {
log.error("[exceptionHandle] ex", e);
return new ErrorResult("EX", "내부 오류");
}
@GetMapping("/api2/members/{id}")
public MemberDto getMember(@PathVariable("id") String id) {
if (id.equals("ex")) {
throw new RuntimeException("잘못된 사용자");
}
if (id.equals("bad")) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("잘못된 입력 값");
}
if (id.equals("user-ex")) {
throw new UserException("사용자 오류");
}
return new MemberDto(id, "hello " + id);
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
static class MemberDto {
private String memberId;
private String name;
}
}@ExceptionHandler 적용 방식
- 우선순위
- 우선 스프링에서는 항상 자세한 것이 우선순위를 가진다.
- 부모 예외 클래스가 있고 그걸 상속받은 자식 예외 클래스가 있는데, 둘 다
@ExceptionHandler로 명시되어 있다고 가정해보자.- 자식 예외가 호출되면 부모 예외도 함께 호출 대상이 된다.
- 물론 더 자세한 것이 우선 순위를 가지기 때문에 자식 예외에 대한
@ExceptionHandler만 호출된다.
- 당연하지만 부모 예외만 호출되면 부모 예외에 대한
@ExceptionHandler만 호출된다.
- 다양한 예외
@ExceptionHandler하나에 여러 개의 예외를 명시할 수도 있다.- 예시 :
@ExceptionHandler({AException.class, BException.class})
- 생략 가능
@ExceptionHandler에 예외를 명시하지 않아도 된다.- 생략하면 해당 예외 처리 메소드의 파라미터인 예외가 지정된다.
테스트
- 이제
http://localhost:8080/api2/members/bad를 호출하면 아래와 같은 값이 반환된다.
{
"code": "BAD",
"message": "잘못된 입력 값"
}HTML 오류 화면
ModelAndView를 사용해서 오류 화면을 응답하는 데 사용할 수도 있다.
@ExceptionHandler(ModelAndViewDefiningException.class)
public ModelAndView ex(ModelAndViewDefiningException e) {
log.info("exception e", e);
return new ModelAndView("error");
}API 예외 처리 - @ControllerAdvice
@ExceptionHandler를 사용해서 예외를 깔끔하게 처리할 수 있게 되었다.- 하지만 컨트롤러 안에 정상 코드와 예외 처리 코드가 섞여있다.
@ControllerAdvice또는@RestControllerAdvice를 사용하면 분리할 수 있다.
어드바이스 생성하기
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice
public class ExControllerAdvice {
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
@ExceptionHandler(IllegalArgumentException.class)
public ErrorResult illegalExHandle(IllegalArgumentException e) {
log.error("[exceptionHandle] ex", e);
return new ErrorResult("BAD", e.getMessage());
}
@ExceptionHandler
public ResponseEntity<ErrorResult> userExHandle(UserException e) {
log.error("[exceptionHandle] ex", e);
ErrorResult errorResult = new ErrorResult("USER-EX", e.getMessage());
return new ResponseEntity<>(errorResult, HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
@ExceptionHandler
public ErrorResult exHandle(Exception e) {
log.error("[exceptionHandle] ex", e);
return new ErrorResult("EX", "내부 오류");
}
}@ControllerAdvice
@ControllerAdvice는 대상으로 지정한 여러 컨트롤러에@ExceptionHandler와@InitBinder기능을 부여해준다.@ControllerAdvice에 대상을 지정하지 않으면 모든 컨트롤러에 적용된다. (글로벌 적용)@RestControllerAdvice는@ControllerAdvice와 원리는 같다.- 다만
@ResponseBody가 추가되어 있는 것이 차이점이다. @Controller와@RestController의 차이점과 같다.
- 다만
@ControllerAdvice를 지정하는 방법은 여러 가지가 있다.- 글로벌 기준
@ControllerAdvice
- 애노테이션 기준
@ControllerAdvice(annotations = RestController.class)
- 패키지 기준
@ControllerAdvice("org.example.controllers")- 패키지 기준으로 명시하면 해당 패키지 하위의 패키지에 있는 컨트롤러에도 적용된다.
- 클래스 기준
@ControllerAdvice(assignableTypes = {ControllerInterface.class, AbstractController.class})- 궁금해서 테스트해보니까
@ControllerAdvice에 부모 컨트롤러만 지정하고, 자식 컨트롤러에서 예외 발생시키니까 적용되긴 한다.
- 글로벌 기준
- 더 자세한 설명은 공식 문서를 참고하자.